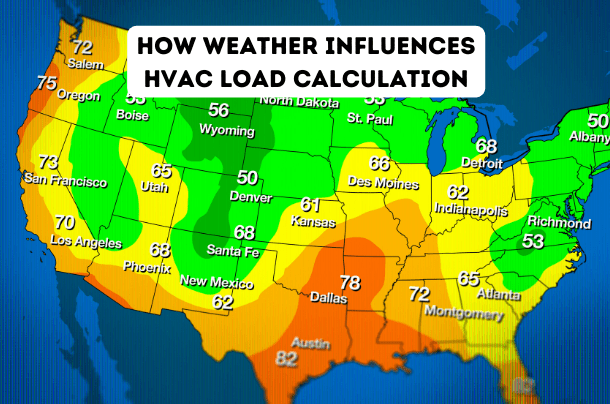
How Weather Influences HVAC Load Calculation
In our previous blog post, we talked about how building envelopes affect in HVAC load calculations. In this blog, we shift our focus to another pivotal factor—climate.
We want to explore how the weather affects HVAC systems. Think of it like picking clothes for the day. You wouldn’t wear a winter jacket in summer or shorts in winter. Understanding the weather helps your HVAC system work well, keeping your place comfy, just like wearing the right clothes for the day. It’s about making sure your system fits the weather, so you’re always feeling just right indoors.
In the context of HVAC load calculation, climate analysis refers to the comprehensive examination and understanding of the specific weather conditions of a geographical location where a building is situated. This analysis takes into account various climatic factors, such as temperature ranges, humidity levels, seasonal variations, and other meteorological elements that can impact the heating and cooling requirements of a building.
But what is the purpose of climate analysis in HVAC load calculation?
The reason being is that it gathers data that helps designers and engineers determine the correct amount of heating and cooling needed to maintain optimal indoor conditions throughout the year. By considering the unique characteristics of the climate, HVAC systems can be tailored to efficiently and effectively handle the varying thermal loads imposed by different weather conditions. At ProCalcs, we make sure to utilize ASHRAE weather data from various weather locations around the country. ASHRAE’s reliable weather data contributes to the accuracy of our load calculations, allowing us to better predict heating and cooling requirements based on the intricacies of local climates.
How does the weather affect HVAC systems?
Climate serves as one of the foundations for HVAC load calculations. In a more technical discussion, climate directly impacts the sensible, latent, and total heat loads in an HVAC load calculation:
– Sensible Heat Load: Sensible heat refers to the heat that causes a change in temperature. In extreme temperatures, especially during heatwaves or cold snaps, the sensible heat load is significantly affected. For example, in a scorching summer day with temperatures reaching 100°F (38°C), the sensible heat load increases due to the higher temperature difference between the outdoor and desired indoor temperatures.
– Latent Heat Load: Latent heat is associated with humidity changes. Extreme temperatures can affect the moisture content in the air, impacting the latent heat load. In extremely cold conditions, the air tends to be dry, leading to a lower latent heat load. Conversely, in humid and hot conditions, the latent heat load increases.
– Total Heat Load: The total heat load is the sum of sensible and latent heat loads. Temperature extremes influence both components, making it a critical consideration. During a heatwave, the total heat load is higher due to elevated sensible heat from the high outdoor temperature, and in a humid environment, the latent heat load contributes significantly to the total load.
The unique characteristics of a region’s climate, including temperature ranges, humidity levels, and seasonal variations, directly impact the heating and cooling demands placed on a building.
- Temperature Extremes:
In regions with extreme temperatures, whether hot or cold, HVAC systems need to be robust enough to handle peak loads during the most challenging weather conditions. Climate analysis helps identify temperature extremes, allowing HVAC designers to select equipment and design systems that perform optimally under these conditions.
- Seasonal Variations:
Seasons bring about fluctuations in temperature and humidity. A thorough climate analysis considers these seasonal variations to ensure HVAC systems are designed to meet year-round comfort requirements.
Heating and cooling loads vary significantly between seasons, and a precise understanding of these changes is vital for accurate load calculations.
- Humidity Considerations:
Climate analysis goes beyond temperature considerations to include humidity levels. High humidity can impact the perceived comfort, and HVAC systems must be equipped to address both temperature and humidity control.
Through the incorporation of climate data into load calculations, the bonus of an overall energy efficiency of HVAC systems is attained. By tailoring designs to specific climate conditions, designers can implement strategies that minimize energy consumption.
Other than that, climate analysis plays a crucial role in designing HVAC systems that are also capable of providing comfort under a range of environmental circumstances. It allows HVAC professionals to select appropriate equipment, size ductwork, and design systems that can handle peak loads during extreme weather conditions. The goal is to create HVAC systems that are well-adapted to the specific climate of a location, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.
For all your HVAC Design needs, email us at tom@procalcs.net. Our team of experienced professionals is ready to assist you in optimizing your HVAC system for maximum efficiency and comfort. Whether you’re planning a new construction project or considering upgrades to your existing system, we’ve got you covered.